A quickly spreading ransomware attack called “Petya” has affected more than 12,000 machines running older versions of MS Windows worldwide. This new ransomware has hit high-profile targets in multiple countries, including the United States. While Petya has not infiltrated as many machines as ransomware WannaCry did in May, it is more dangerous and has the power to create more damage. Here is what you need to know about this potentially dangerous cyberattack and how to keep you and your organization safe.
Petya is a variation of ransomware. It exploits a vulnerability in computer systems known as Eternal Blue, which was leaked online last April by a mystery group of hackers. This vulnerability was also used in May to spread the WannaCry ransomware, which affected hundreds of thousands of computers in more than 150 countries. Like the WanaCry Ransomware attack, Petya targets older versions of Microsoft Windows that are not up to date. Microsoft provided a patch for this in March, and you can learn more about it here at Microsoft's blog.
WHERE IT STARTED & WHO IS AFFECTED
It is believed to have originated in the Ukraine where hackers first targeted a Ukrainian tax accounting software company. It has since spread quickly to approximately 64 countries. Several large private companies have confirmed that they were struck by the attack, including American pharma Merck, Danish shipping AP Moller-Maersk, French multinational Saint-Gobain, Mondelez International and more.
WHAT YOU NEED TO LOOKOUT FOR
Source: Malwarebytes Labs, Petya – Taking Ransomware To The Low Level
Petya is delivered via a scam job application phishing email. The email is received with a Dropbox link, where a malicious ZIP is hosted. This initial ZIP contains two elements:
- A photo of a young man, purporting to be an applicant (a publicly available stock image)
- An executable, pretending to be a CV in a self-extracting archive or PDF (a malicious dropper in the form of a 32bit PE file)
IMPORTANT: Do not try to run the petya_exe file. If you do, a User Account Control pops up this alert: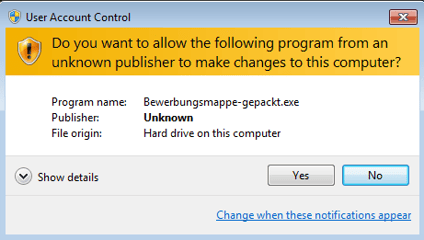
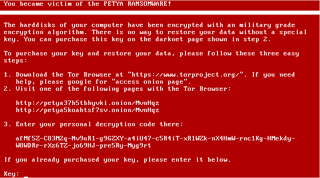
If you were to deploy the application, your computer will crash. When it restarts, you will eventually reach a red screen with a ransom note and all information necessary to process a payment:
SHOULD YOU PAY?
Cybersecurity researchers identified a Bitcoin address to which the attackers are demanding a payment of $300 from their victims. At least some appear to have paid the ransom (As of Wednesday morning, the address had logged 45 transactions. The email address used by the attackers was shut down, removing the possibility a victim could restore access to their computer networks, even once the ransom is paid.
HOW TO PROTECT YOURSELF AND YOUR ORGANIZATION FROM ATTACKS LIKE PETYA
Source: Madeline Purdue, of USA TODAY (How to protect your Windows computer from the Petya ransomware attack)
- Download patches – One of the best things you can do to protect yourself from these attacks is to download the patches Microsoft provides during updates. Microsoft released a patch to protect against the vulnerability on its Windows XP system in March. Earlier this month, it issued more patches for older Windows operating systems, citing the "elevated risk for destructive cyber attacks."
- Back up your computer – You should always back up your computer just in case a ransomware attacks your computer, so you have copies of your files in another location, like an external hard drive or in the cloud.
- Install protection programs – You should download protection programs that not only fight attacks but also notify you when there is a threat to your computer. These programs include firewalls, anti-virus programs and other protective software. They can alert you if malware is trying to encrypt your files and what they are doing to stop it.
- Don’t click on anything suspicious – Some of these attacks occur because of phishing emails. These emails are designed to make you think they are legitimate, but install malware on your computer once you open them. Often, there is a typo in the name of the company or person supposedly sending you the email. It can be as little as one letter changed from their actual name.
- Protect yourself when using public WiFi – When using public Wi-Fi, you are viewable to everyone else using that network. You want to make sure you change your security settings on your computer when on a public network. Usually, computers will ask you automatically if you want to be viewable on the network, but check your security settings just to be sure you are not set to public.
To Our Valued Clients - You're Safe!
Please be aware that LANTIUM is constantly monitoring and updating operating systems as a service to all of our managed services clients. We understand the seriousness of this and all other cyberattacks and the effect it can have on your business.
Although this ransomware attack has proven to be successful globally, we do not foresee any issues in the environments of our managed service clients due to our ongoing efforts to patch workstations and servers regularly.
How Do I Know if I Have Been Infected?
Sometimes even taking every precaution is not enough for IT security, which is why knowing what to look for and how to detect the symptoms of a compromised computer is important to ensure your safety. Read our recent post, 5 Symptoms of a Compromised Computer, to know if you have been infected and if your data and network is at risk.
How to Protect Your Business from Ransomware:
Practicing good cyber hygiene is the best way to protect yourself, your workplace, and data from cyberattacks. A few technical considerations are listed below. All of them you may do on your own or contact LANTIUM for assistance:
- Enable strong spam filters, and scan all inbound and outbound emails with filters
- Configure firewalls to block access to known malicious IP addresses
- Patch all operating systems, software, firmware
- Set antivirus and antimalware programs to scan automatically
- Manage use of sensitive accounts on the principle of least privilege
- Consider disabling Remote Desktop Protocol
- Use application whitelisting and backup data regularly
- Conduct annual penetration testing
The truth is, there’s no excuse for leaving yourself or your business exposed. Please read our recent post, Seven Simple Habits to Protect Your Business from Ransomware, for things to do now for basic data breach prevention, minimize risk, and to keep you, your end users and business safe.
What to Do if You’re Infected:
Panic and worry can be overwhelming once you realize that your computer may have been compromised. However, it’s not over for your computer and all of your files. If you believe you have been infected by a virus, trojan, worm, ransomware, or cryptolocker, there is still a chance to restore your computer to the state it was prior to infection, quickly, and without further damage or loss of productivity.
If you believe your computer may be infected, or if your organization has had IT security and performance issues in the past, Lantium can help! Our Critical Care support team is available for our clients 24x7x365.
Interested in learning more about security audits, proactive monitoring, data backup, or how to make your business and its data more secure? Schedule a free call with our experienced security consultants today: 



